Osteochondrosis is a spinal disease in which degenerative processes occur in cartilage and joints. It is characterized by thinning and a decrease in the elasticity of the intervertebral discs.
Features of the disease
The disease mainly affects the elderly. Although scientists note that the manifestations of the disease are increasingly aging in the thirties or earlier. This indicates that the disease is very young.

Intervertebral discs provide shock-absorbing function, but are unable to cope with disease. A person suffering from osteochondrosis almost always complains of pain, and the pain can manifest itself locally and remotely. Man feels stiffness in movements, lethargy and fatigue.
The pain mainly manifests itself in the affected part of the disease.
Localization and types of pathology
There are 4 types of osteochondrosis, depending on which part of the spine is damaged by pathology:
- Cervical osteochondrosis. . . Occurs when there are pathological changes in the cervical spine. The vertebrae become brittle, the load on the cervical spine increases, which can lead to thyroid dysfunction and narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the brain.
- Chest osteochondrosis. . . Pathological changes occur in the spine. Because the thoracic vertebrae are protected by less mobile and stronger muscles, patients are less likely to be diagnosed than other types. These symptoms are similar to cardiovascular disease.
- Lumbar osteochondrosis. . . This type is the most common. Because the waist has the greatest load.
- Combined. . . Occurs when several parts of the spine are damaged at once.
In addition, the disease can affect other joints. They often suffer:
- Shoulder joint. . . As a rule, the disease is caused by the transition of cervical spine osteochondrosis to the shoulder joint.
- Hip joint. . . Occurs due to changes in cartilage tissue and lack of fluid between the joints.
- Knee joint. . . Chondrosis can manifest itself in 3 forms:
- Koenig's disease, in which cartilage tissue is affected.
- Larsen-Johansson disease, in which changes occur in the joint above the knee.
- Osiaod-Schlatter disease is associated with changes in the tibia.
Classification and degree of manifestation of the disease
The disease can be classified according to the degree of manifestation. At the same time, it is difficult to determine the degree of the disease before the onset of characteristic pain. There are 4 degrees of manifestation of the disease:
- The initial stage of disease development. Occurs due to displacement of the spinal disc associated with weight lifting. It is characterized by unstable pain sensations. At this stage, the disease is difficult to diagnose, but easily treated.
- This stage is characterized by the gradual destruction of the intervertebral disc, drying and loss of shock-absorbing properties. This causes an increase in tension in the blood vessels and nerve endings. The pain intensifies and manifests itself with the most physical force and sudden movements. Treatment of the disease at this stage is conservative.
- Anulus fibrosis is destroyed and an intervertebral hernia occurs. There is a deformity of the spine. Pain is significant. Treatment is possible only with surgery.
- At this stage, the vertebrae grow together due to the formation of osteophytes. There is a pinch in the spinal tissues, the vertebrae lose mobility and restrict a person's movement. At this stage, the disease can lead to disability and is no longer suitable for treatment.
Typical symptoms
Each type of disease has its own symptoms. For example, cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by:
- Pain in the arms and shoulder girdle.
- Headache.
- Dizziness and spots in front of the eyes.
- Blood pressure instability.
- Loss of sensitivity in the fingers.
- The sound of the ear.
Symptoms are characteristic of thoracic pathology:
- Pain in the heart area.
- Pain in the hypochondria.
- Lack of air due to acute pain of shooting nature.
When the disease is localized in the lower back, there are:
- Pain in the waist.
- Decreased sensitivity in the legs.
- Radiation pain in the legs.
- Disorders of the pelvic organs.
There are also common symptoms that do not depend on the location of the disease:
- Back pain.
- Muscle spasms.
- Restriction of movement.
- Changes in pain syndrome due to load and sudden movements.
- Harmony of limbs.
- Rapid fatigue.
- Decreased sensitivity of the extremities.
Symptoms and manifestations of osteochondrosis
The first signs of the disease begin to appear in the early stages of development. These include:
- Swelling and pain in the lower back after lying in a position for more than half an hour.
- Pain in the back after a long sitting.
- The need to lie down after waking up and the impossibility of waking up immediately.
- The crisis behind is felt.
- Decreased sensation of gas bumps and limbs.
- Unpleasant sensations when bending the back.
- General weakness.
- Disorders of reproductive function and internal organs.
Osteochondrosis can also manifest itself with pain during weight lifting and physical activity.
Methods of pathological diagnosis
Complex methods are used to diagnose osteochondrosis. These include:
Preliminary examination and inquiry of the patient:
- Complaints, interview a patient to clarify the timing of the onset of symptoms.
- Examination of the patient's body, study of posture, gait and movement.
- Palpation of problem areas.
- Determination of pain sensitivity.

Instrumental diagnostics:
- X-ray to help determine the deformation of the intervertebral discs.
- MRI to determine the presence and location of a herniated disc.
- According to computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging is similar to imaging, but has a higher degree of radiation.
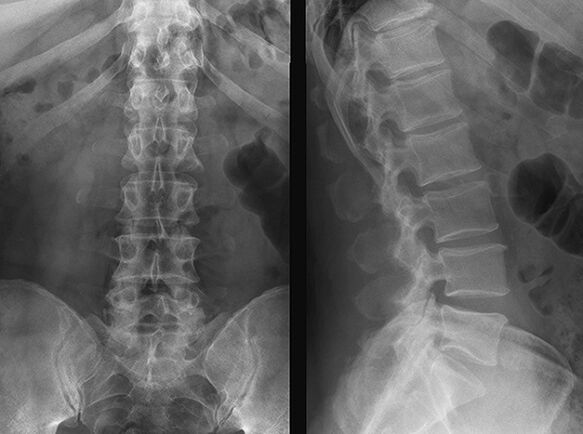
Methods of treatment of the disease
After performing diagnostic procedures and diagnosing osteochondrosis, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
Since osteochondrosis can only be treated in the early stages of development, all major measures are mainly aimed at relieving pain. To do this, apply:
- Medication.
- Physiotherapy.
- Manual therapy.
- Masotherapy.
- Diet.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used as drug treatment. These are aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process in the diseased area and preventing pain.
Chondroprotectors are also used to repair cartilage tissue. Immunostimulants and vitamin complexes are used to maintain the normal functioning of the body.
Physiotherapy methods are aimed at relieving pain, normalizing metabolic processes in the affected areas, improving blood circulation, eliminating inflammation and edema. These include:
- Acupuncture.
- Magnetic therapy.
- Electrophoresis.
- Laser therapy.
- Paraffin treatment.
Physiotherapy techniques help shorten treatment times and have fewer side effects than medications.
Manual therapy is a dosing effect of the doctor's hands on the affected areas of the lower back to eliminate the limitations that interfere with the normal functioning of joints, muscles and ligaments.
Therapeutic massage should be performed only by a specialist and aims to relieve muscle tension, restore displaced spine and normalize blood circulation. The procedure should be performed at least three times a week.
The diet for osteochondrosis is to normalize weight, improve blood circulation, replenish collagen, eliminate calcium and mineral deficiencies, and help manage fluid and salt intake. The diet should be balanced and rich in plant foods. Coffee and strong tea, foods rich in salt and sugar, carbonated beverages and fatty foods should be excluded in the fight against osteochondrosis.
During these procedures, the disease can be corrected and surgery is required only in difficult stages.
Preventive measures
To prevent this disease, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle and give up harmful habits, exercise, use an orthopedic mattress and a pillow for bed, avoid uncomfortable shoes, it is better to use orthopedic shoes.
You also need to follow your diet and maintain a healthy weight. It is necessary to spend time on exercises that help to normalize blood circulation by staying in a static position for a long time.
You can also do sanatorium treatment and general strengthening massage for the prevention and treatment of the disease.

























